Sialadenitis Treatment
- Painful swelling in the affected gland
- Redness and tenderness around the mouth, jaw, or neck
- Dry mouth or unpleasant taste
- Fever or general feeling of being unwell
- Difficulty opening the mouth or swallowing
Home » Conditions » Sialadenitis Treatment
Expert Care for Swollen and
Infected Salivary Glands
Sialadenitis is an infection or inflammation of the salivary glands that can cause swelling, discomfort and difficulty eating or speaking. Although it may sometimes be mild, it can also develop into a persistent or painful problem that requires medical attention. At Head2Neck, we provide specialist diagnosis and tailored sialadenitis treatment, ensuring patients receive care that addresses both the underlying cause and long-term prevention.
What is Sialadenitis?
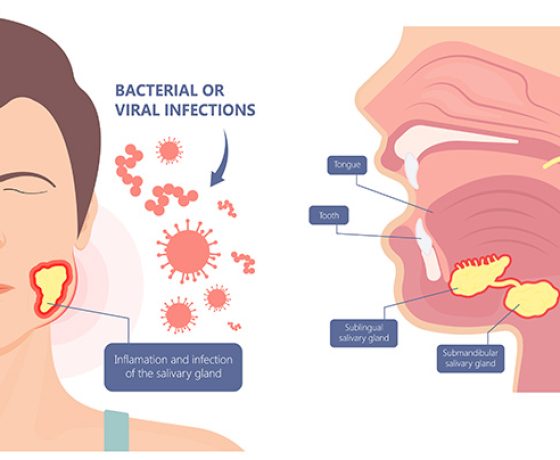
Sialadenitis is a condition where one or more of the salivary glands become inflamed, often due to a bacterial or viral infection. The parotid and submandibular glands are most frequently affected. In some cases, reduced saliva flow or a blocked salivary gland caused by stones (sialolithiasis) can trigger infection.
The infection may present as an acute episode, developing suddenly, or as a chronic condition with repeated flare-ups. Understanding the cause is essential to selecting the most appropriate salivary gland treatment.

Common Symptoms
The symptoms of salivary gland infection can vary depending on whether the condition is acute or chronic. Typical signs include:
- Painful swelling in the affected gland
- Redness and tenderness around the mouth, jaw, or neck
- Dry mouth or unpleasant taste
- Fever or general feeling of being unwell
- Difficulty opening the mouth or swallowing
- Pus discharge into the mouth in more severe cases
Causes and Risk Factors
Sialadenitis occurs when the natural flow of saliva is obstructed or when infection takes hold in a vulnerable gland. Common causes and risk factors include:
Salivary gland stones blocking the ducts
Dehydration reducing saliva production
Poor oral hygiene
Viral infections such as mumps
Reduced immunity, including in older adults
Post-operative changes that affect saliva flow
Patients with recurrent salivary gland swelling or chronic infections may require specialist assessment to rule out underlying salivary gland disease.
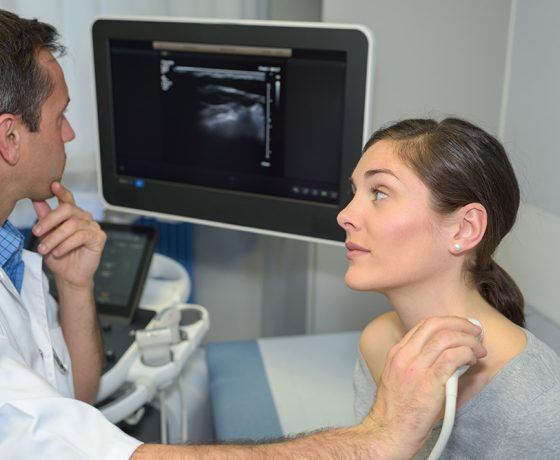
When Should I Seek Medical Attention for Sialadenitis?

While mild swelling or discomfort may improve with hydration and self-care, medical assessment is important if symptoms persist or worsen. You should see a specialist if you develop severe pain, fever, pus discharge, or if swelling recurs frequently.
Difficulty opening the mouth, problems swallowing, or repeated infections are also signs that professional diagnosis and treatment are needed. Early intervention can prevent complications and reduce the likelihood of chronic salivary gland disease.
Diagnosis at Head2Neck
Accurate diagnosis is essential to managing sialadenitis effectively. At Head2Neck, diagnosis begins with a careful medical history and clinical examination by Consultant Surgeon Mr Konstantinos Karavidas. Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, MRI, or CT may be used to identify salivary duct obstruction or confirm the presence of stones.
Where necessary, we employ sialendoscopy, a minimally invasive technique that allows direct visualisation of the ducts. This approach can be both diagnostic and therapeutic, helping to confirm the cause while also addressing it.
Treatment Options for Sialadenitis
The choice of sialadenitis treatment depends on the severity of symptoms and the underlying cause. At Head2Neck, we provide a comprehensive range of treatment options:
Conservative Management
In mild cases, infections may be treated with antibiotics, improved hydration, salivary gland massage and warm compresses. These measures help stimulate saliva flow and reduce discomfort.
Sialendoscopy
This minimally invasive approach can clear a blocked salivary gland by removing stones or debris. It is highly effective in cases of recurrent swelling or obstruction and often avoids the need for open surgery.
Surgical Treatment
Where conservative measures or sialendoscopy are not sufficient, surgical options may be recommended. This could involve the removal of stones or, in rare cases, the removal of the affected gland. At Head2Neck, we use advanced surgical techniques to minimise disruption and ensure safe, effective outcomes.
If you would like to understand more about the treatment journey, including what to expect before and after care, please see our Patient Info page.
Why Choose Head2Neck for Your Sialadenitis Treatment?
Choosing the right specialist for salivary gland infection treatment can make a significant difference in recovery and long-term outcomes. At Head2Neck, we offer:
- Specialist expertise from a consultant head and neck surgeon with extensive experience in salivary gland treatment
- Access to advanced techniques, including sialendoscopy and robotic surgery
- Personalised care that considers both the immediate infection and the prevention of recurrence
- Convenient clinics across London, Essex, Hertfordshire and Bedfordshire
- A patient-centred approach, combining surgical precision with clear communication and supportive aftercare






What Our Patients Say
I’ve been seeing Mr Karavidas since Feb 25 and have had several consultations and 2 surgical procedures at Cobham Clinic. He is extremely thorough and makes sure you understand every step of what’s happening with any diagnosis and procedure. Fantastic service.
A.B. 08/06/2025
Clear explanations, very reassuring throughout consultations and proceedure. Mr Karavidas made me feel at ease, his professionalism immediately evident. Highly recommended.
N.A. 10/03/2025
I was beyond impressed by Mr Karavidas. He took the time to listen to all my concerns, reassured me & gave the very best advice. He was friendly and put me at complete ease. I was very well taken care of and cannot thank him enough. I highly recommend!
V.G. 19/02/2025
Two lower wisdom teeth removal. Couldn’t fault the service. Excellent and extremely responsible after care from Mr Karavidas.
J.L. 02/12/2024
My experience with Dr Karavidas and his team was exceptional. I felt extremely cared for and informed throughout and could not have asked for more. To top it off we had a fully successful outcome after an oral procedure which means I can eat again! Thank you so much.
S.J. 21/10/2024
I’ve been seeing Mr Karavidas since Feb 25 and have had several consultations and 2 surgical procedures at Cobham Clinic. He is extremely thorough and makes sure you understand every step of what’s happening with any diagnosis and procedure. Fantastic service.
A.B. 08/06/2025
Clear explanations, very reassuring throughout consultations and proceedure. Mr Karavidas made me feel at ease, his professionalism immediately evident. Highly recommended.
N.A. 10/03/2025
I was beyond impressed by Mr Karavidas. He took the time to listen to all my concerns, reassured me & gave the very best advice. He was friendly and put me at complete ease. I was very well taken care of and cannot thank him enough. I highly recommend!
V.G. 19/02/2025
Two lower wisdom teeth removal. Couldn’t fault the service. Excellent and extremely responsible after care from Mr Karavidas.
J.L. 02/12/2024
My experience with Dr Karavidas and his team was exceptional. I felt extremely cared for and informed throughout and could not have asked for more. To top it off we had a fully successful outcome after an oral procedure which means I can eat again! Thank you so much.
S.J. 21/10/2024

Frequently Asked Questions
What is the fastest way to treat a salivary gland infection?
The quickest way to manage a salivary gland infection is with antibiotics to target the bacteria, alongside simple measures such as hydration, warm compresses and massage to improve saliva flow. If stones or blockages are present, specialist treatment like sialendoscopy may be needed to resolve the problem effectively.
Can sialadenitis go away on its own?
Mild cases may improve with rest, good hydration and stimulating saliva flow naturally. However, many infections require medical treatment and delaying care can lead to more persistent or severe symptoms.
How serious is sialadenitis?
Most cases are straightforward to treat, but the condition can become serious if infection spreads or if it recurs frequently. Specialist assessment ensures the underlying cause, such as a stone or blockage, is properly managed.
What are the symptoms of salivary gland infection?
Typical signs include swelling, pain, tenderness, fever, dry mouth and an unpleasant taste. More advanced infections can cause pus discharge into the mouth or significant discomfort when opening the jaw.
What causes swollen salivary glands?
Swelling is often caused by a stone blocking the duct or an infection in the gland. Other factors such as dehydration, poor oral hygiene, or reduced immune function can also contribute to salivary gland inflammation.
How is sialadenitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis usually begins with a clinical examination and review of symptoms by a specialist. Imaging, such as ultrasound or MRI, can confirm stones or blockages, and sialendoscopy may be used to see directly into the ducts.
How long does sialadenitis last?
With appropriate treatment, acute sialadenitis often improves within a week or two. Chronic or recurrent infections may last longer and require targeted procedures to prevent further flare-ups.
Is surgery needed for sialadenitis?
Surgery is not always necessary, as many cases respond to conservative care or sialendoscopy. It may only be considered in complex or persistent cases where the gland is severely damaged or repeatedly infected.
What is the difference between sialadenitis and sialolithiasis?
Sialadenitis refers to inflammation or infection of a salivary gland, often linked to bacteria or reduced saliva flow. Sialolithiasis describes the presence of salivary stones, which can block ducts and trigger sialadenitis episodes.
Can dehydration cause sialadenitis?
Yes, dehydration can reduce saliva production and make it easier for bacteria to grow in the salivary glands. Staying hydrated is an important step in preventing sialadenitis and reducing the risk of stone formation.
Is sialadenitis contagious?
Sialadenitis itself is not contagious, as it is usually linked to blockages or reduced saliva flow. However, if the underlying cause is a viral infection such as mumps, that infection can spread to others.
Book a Consultation with Mr. Karavidas


